Calculate the Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) using the patient’s serum creatinine level, age, race and sex.
Formula:
The IDMS-traceable MDRD study equation
GFR = 175 × (SCr)-1.154 × (age)-0.203 × (0.742 if female) × (1.212 if Black)where SCr = serum creatinine in mg/dL
The CKD-EPI formula
Black female
If SCr < 0.7GFR = 166 × (SCr/0.7)-0.329 × 0.993age
If SCr > 0.7GFR = 166 × (SCr/0.7)-1.209 × 0.993age
Black male
If SCr < 0.9GFR = 163 × (SCr/0.9)-0.411 × 0.993age
If SCr > 0.9GFR = 163 × (SCr/0.9)-1.209 × 0.993age
Non-Black female
If SCr < 0.7GFR = 144 × (SCr/0.7)-0.329 × 0.993age
If SCr > 0.7GFR = 144 × (SCr/0.7)-1.209 × 0.993age
Non-Black male
If SCr < 0.9GFR = 141 × (SCr/0.9)-0.411 × 0.993age
If SCr > 0.9GFR = 141 × (SCr/0.9)-1.209 × 0.993age
The Mayo Quadratic Formula
If SCr < 0.8 mg/dL, use 0.8 mg/dL for SCrGFR = e(1.911 + 5.249/SCr – 2.114/SCr2 – 0.00686 × age – (0.205 if female))
Principle:
Creatinine is actively secreted in small amounts in the body resulting in GFR determined through creatinine clearance typically being overestimated by 10-20%. Despite its limitations, creatinine clearance still provides an acceptable estimation of GFR due to its ease of measurement when compared to inulin clearance. Below are three formulas often used for estimating GFR through serum creatinine.
Interpretation:
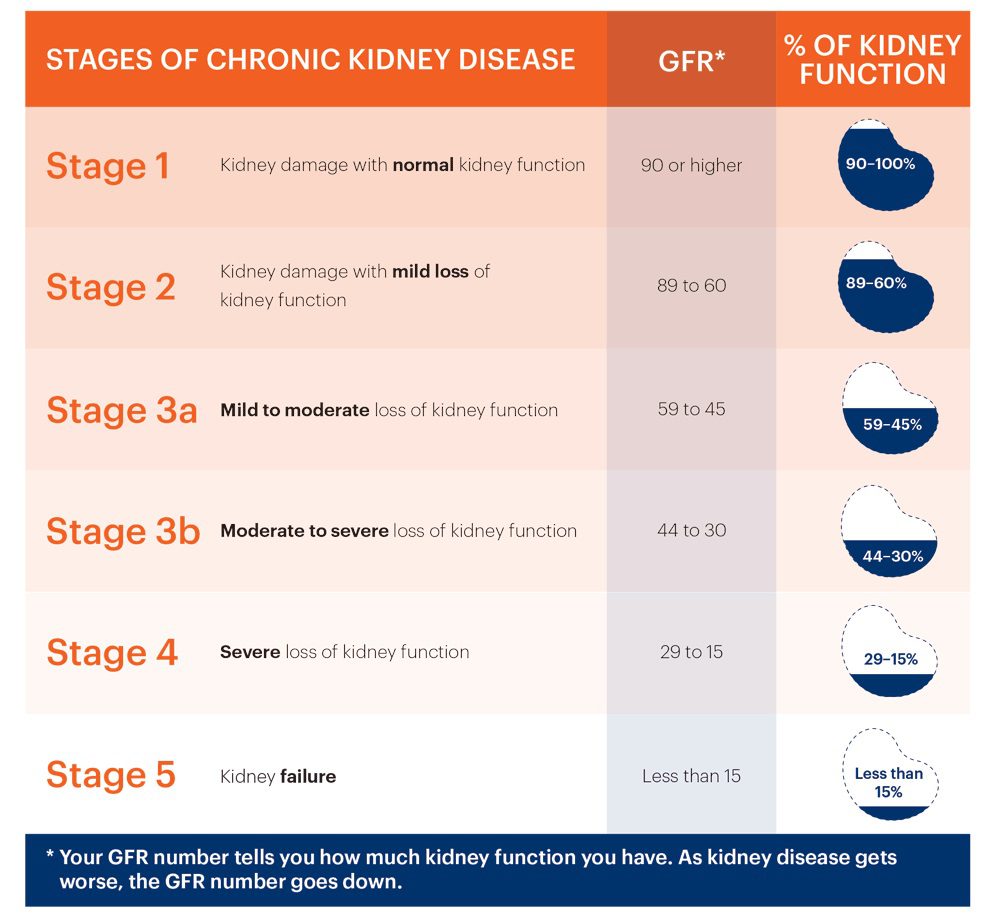
Credit to the National Kidney Foundation